Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Screening the Possible Mental Health Issues in Adolescents
Authors: Aadesh Gupta, Harsh Patil, Aditya Mullankara, Pushpal Hedau
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.57991
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The abstract reflects the collective decision of a group of computer engineering students who are passionate about exploring the intersection of technology and clinical psychology for young people. They see the transformative potential of data from insights to use technology to increase the efficiency and accessibility of health promotion for young people. The basis of their approach is a commitment to technological development and they aim to create advanced tools and platforms that engage young people digitally, leading to mental tests, that are more supportive and effective. Familiar with many aspects of youth health, these students are eager to collaborate. They believe that collaboration with professionals in fields such as psychology, social work, medicine and education is essential to develop solutions to mental health problems and mental challenges. Students emphasized ethical considerations such as privacy, consent, and technology provision at the center of their efforts. Ultimately, these briefs demonstrate their firm belief in the potential of computer engineering expertise to shape the future of youth mental health support, as well as the goal of promoting youth health and recovery through assessment, better use, and empowerment.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
This report provides an overview of the importance of examining mental health problems in youth, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and intervention during this critical period of development. It explores the most common and associated mental health issues in young people, providing insight into the situations they face. Additionally, the report examines various analysis methods and tools to evaluate their effectiveness and limitations. She talks about creating a supportive environment that encourages young people to open up about mental health issues and collaboration between schools, health professionals and families in the process.
This effort stems from the awareness of the potential that exists in all young people and the resilience they possess. Adolescence is a difficult time, but it is also an important time of growth, self-discovery, and vulnerability. Screening teens for mental health issues not only meets their current needs but also allows them to develop into well-rounded adults. Early intervention and support is the beacon of hope that guides young people through the uncertainty, anxiety, and self-doubt that often arise during this period. As caregivers, educators, and therapists, we have the right to give young people the tools and information they need to overcome these challenges. Investing in their health can plant the seeds for a better future, enabling young people to thrive, achieve their dreams and contribute to healthy, loving and empowered lives. In this way, we are motivated by the belief that all young people can thrive when given the support and understanding they need.
II. NEED OF THE STUDY
The increasing number of mental health problems among young people, as well as the current lack of screening, is a pressing concern. Delayed or missed diagnosis can have long-term impacts on young people who are at higher risk due to mental health stigma and medical disparity. In order to solve this problem, it is necessary to complete the path, determine the truth and support the youth, and ultimately create a healthy and stronger youth. This study was designed to create a standardized, comprehensive assessment involving schools and health services to support early diagnosis and intervention. It also aims to create awareness and education programs to eliminate the stigma surrounding youth health and promote a culture of open communication and support in school and family.
Tackling rising mental health issues among young people requires a guide. In addition to standardized testing for schools and health services, collaboration between these organizations needs to be strengthened. Community engagement measures and public awareness programs can help eliminate stigma around youth health and build greater support.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The methodology section delineates the strategic plan and methods employed to conduct the study, encompassing various crucial components. These include the study's scope, the target population, sample selection, data sources, variables under examination, and the analytical framework. The details are outlined as follows:
A. Functional Requirement
- User Management: Administrators can create user accounts with defined roles and permissions, as well as modify or delete accounts as required.
- Screening Protocol Management: Authorized users can create, edit, and oversee standardized screening protocols used in educational institutions. These protocols can be distributed to educators and healthcare providers.
- Data Entry and Storage: Educators and healthcare providers have access to a user-friendly interface for efficient input of screening data. Data security is ensured through encryption and access controls, complying with privacy regulations.
- Reporting and Analytics: The software generates reports, offering aggregated screening data and visualizations, aiding stakeholders in gaining insights into trends and making informed decisions.
- Awareness Campaign Management: Users can create, edit, and schedule awareness campaigns, including the management of educational materials and resources. The software allows targeting specific audiences and tracking campaign effectiveness based on engagement and feedback.
- Feedback Mechanism: A feedback system enables users to report issues, provide suggestions, and seek assistance, with an emphasis on timely responses from administrators.
B. Non-Functional Requirement
- Performance: The system must maintain high responsiveness, ensuring quick loading times and minimal delays, even during peak usage. Response times for data retrieval and reporting should meet acceptable standards for a smooth user experience.
- Security: Robust security measures are imperative to protect sensitive data, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as HIPAA. User authentication and authorization mechanisms control data access.
- Usability: The user interface should be intuitive, user-friendly, and accessible to a diverse user base, including individuals with disabilities. Comprehensive documentation and training materials maximize software usability.
- Reliability: Ensuring system availability with minimal downtime is vital to meet user needs. Regular data backups prevent data loss in unexpected system issues.
- Scalability: The system's design should accommodate future increases in the number of users and data volume, supporting growth.
- Legal and Compliance Requirements: Adherence to data privacy laws and guidelines is essential. Additionally, educational and awareness materials must comply with relevant regulations.
- Maintenance and Support: Detailed plans for ongoing system maintenance, updates, and user support are specified. They include addressing software issues and ensuring adaptability to changing requirements.
- Appendix: This section allows for the inclusion of any additional documents, diagrams, or references pertinent to the project. The SRS serves as a comprehensive guide for software development and project implementation, encompassing functionality, performance, security, usability, and compliance requirements.
C. Theoretical framework
A web application for screening with a chatbot feature is a software program that allows users to screen other users for a variety of purposes, such as employment, dating, or volunteering. The chatbot feature allows users to interact with the application in a natural language way, making it easier to screen a large number of users quickly and efficiently.
The web application typically consists of the following components:
- A database of user profiles
- A chatbot that interacts with users to screen them
- A screening algorithm that matches users based on their profile information and screening results
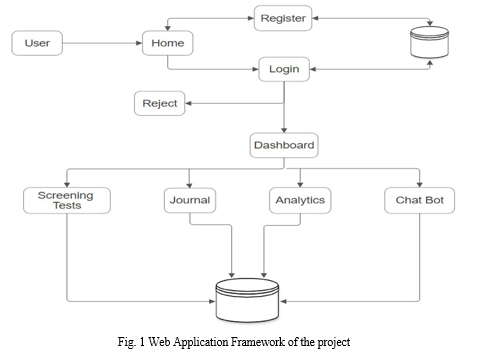
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The project boasts several advantages in addressing mental health issues among adolescents. One key benefit is its capacity for early detection and intervention, employing an effective prediction technique. Additionally, the software facilitates data-driven decision-making by collecting and analyzing screening data, contributing to more informed choices in addressing mental health concerns. A critical aspect of the project is its commitment to standardization. Through the implementation of standardized screening protocols, the assessment process maintains consistency across various educational institutions and healthcare settings.
However, certain limitations should be acknowledged. Privacy concerns arise due to the collection of sensitive mental health data, emphasizing the need for robust privacy measures. The digital divide poses another challenge, as not all adolescents have equal access to technology, potentially limiting their participation in the screening process. User adoption is a crucial factor in the software's effectiveness, as its success heavily relies on widespread acceptance and utilization. Furthermore, the validity of self-reported data by adolescents introduces a potential limitation, as individuals may not always provide completely accurate information regarding their mental health. Despite these limitations, the project's advantages, especially in early detection and data-driven decision-making, highlight its potential to make significant strides in supporting adolescent mental health.
V. ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to thank Mr. Shivaji Vasekar, whose valuable suggestions and guidance were very important in completing our project "Screening the possible Mental Health Issues in Adolescents". Mr. Vasekar's expertise, encouragement and tireless support played a vital role in transforming our ideas into a powerful and innovative force. We would also like to express our gratitude to our university for providing us with the space and resources necessary to help us complete this important project. Teacher support and learning support are important in our education system. We are grateful to the open source community and dedicated developers behind the tools and libraries that support this project. Their spirit of collaboration and commitment to collaboration has been a constant source of inspiration during the development of our projects.
Conclusion
The scope of this project provides a comprehensive framework to address youth mental health issues through systematic screening and stigma reduction. This scope includes clear objectives, deliverables, stakeholders, and activity definitions, as well as a detailed timeline with milestones, a budget allocation strategy, and a risk management plan to ensure smooth implementation. Evaluation criteria, including key performance indicators, produce measurable results to assess the impact of a project. Collaboration with various stakeholders, a comprehensive communication plan, and ethical considerations will guide interactions within the plan. A focus on training and development ensures that people participating in projects are fully qualified. In addition, the scope also addresses long-term sustainability, legal and regulatory compliance, and potential expansion considerations. This holistic approach not only identifies and addresses youth mental health issues, but also creates effective and ethical efforts that build the foundation for lasting positive impact in communities.
References
[1] E. Krisnanik, I. N. Isnainiyah and A. Z. A. Resdiansyah, \"The Development of Mobile-based Application for Mental Health Counseling during the COVID-19 Pandemic,\" 2020 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS), Jakarta, Indonesia, 2020, pp. 324-328, doi: 10.1109/ICIMCIS51567.2020.9354299. [2] K. Park, M. Jung Kim, J. Kim, O. Cheon Kwon, D. Yoon and H. Kim, \"Requirements and Design of Mental Health System for Stress Management of Knowledge Workers,\" 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea (South), 2020, pp. 1829-1832, doi: 10.1109/ICTC49870.2020.9289464. [3] R. Katarya and S. Maan, \"Predicting Mental health disorders using Machine Learning for employees in technical and non-technical companies,\" 2020 IEEE International Conference on Advances and Developments in Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ICADEE), Coimbatore, India, 2020, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ICADEE51157.2020.9368923. [4] Choudhury A, Asan O, Alelyani T. Exploring the Role of the Internet, Care Quality and Communication in Shaping Mental Health: Analysis of the Health Information National Trends Survey. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022 Jan;26(1):468-477. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3087083. Epub 2022 Jan 17. PMID: 34097623. [5] R. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Liao and J. Wang, \"Supervised Machine Learning Chatbots for Perinatal Mental Healthcare,\" 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Human-Computer Interaction (ICHCI), Sanya, China, 2020, pp. 378-383, doi: 10.1109/ICHCI51889.2020.00086.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Aadesh Gupta, Harsh Patil, Aditya Mullankara, Pushpal Hedau. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET57991
Publish Date : 2024-01-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

